
The Fed is trying to encourage more leverage and more debt. Mr. Market is balking, worried either about a reversal of Fed policy, or more inflation, or a selloff in equities, or all of the above.
Bill Bonner, writing today from Baltimore, Maryland
Survive to fight another day.
–Tom Dyson
What’s an investor’s biggest ally? Time.
What’s his biggest enemy? The Big Loss.
Where’s the risk of the Big Loss greatest today? Bloomberg:
Neuberger Berman warned against buying US Treasury bonds on dips, saying the recent selloff could be the beginning of a “surprisingly sustained” move higher in yields [lower prices].
The risk of the Federal Reserve pausing its interest rate reductions, heightened volatility and resilient US growth as well as sticky inflation could push yields on five-year Treasury notes up to about 4.50% over the next three months, said Ashok Bhatia, the firm’s co-chief investment officer for fixed income. They’re yielding about 4.13% now.
“Fixed-income investors ought to brace for more downside volatility,” said Bhatia.
The yield on a 30-year T-bond has already moved up to 4.5% (meaning… the price of the bond has gone down). This is big news. The Fed’s interest rate cut was supposed to be the beginning of more cuts and lower yields.
It tells us that things are moving along more or less as expected (by us) and the Fed can’t control them. The Fed is trying to encourage more leverage… and more debt. Mr. Market is balking… worried either about a reversal of Fed policy… or more inflation… or a selloff in equities… or all of the above.
Whatever else can be said about it, it doesn’t look like we’re turning Japanese… at least not right away. More likely, we face higher interest rates and a big loss in stocks and bonds.
A little perspective…
Over a lifetime, Time and the Big Loss tilt to one direction… and then the other. When you are young, you have plenty of time… and little to lose. As you get older, time runs short… and the danger of the Big Loss grows larger.
Here at BPR, most of our subscribers are over 50. For them, as for us, avoiding the Big Loss is a major concern. Time can take care of itself.
Charlie Bilello spells out how time works for a saver:
What would $5k invested each year grow to by the age of 65 (assuming 8% annual return)? Beginning at…
- Age 25: $1.30 million
- Age 30: $862k
- Age 35: $566k
- Age 40: $366k
- Age 45: $229k
- Age 50: $136k
Bilello hammers away:
To achieve the biggest gains, extend your time horizon whenever possible. Median growth of $100k invested in the S&P 500 over…
- 1 Month: $101k
- 1 Year: $113k
- 3 Years: $138k
- 5 Years: $173k
- 10 Years: $270k
- 20 Years: $820k
- 30 Years: $2.27 million
But it only works if you don’t get wiped out somewhere along the way. Then, you’d have to start all over again. And after age 50… the runway gets short.
Charlie goes on to show how the taxman can help. The difference between saving in a taxable account and saving in a Roth IRA can be substantial. Over 40 years, at $7,000 per year, it can add about $730,000 to your account.
As cynicalists, we are skeptical of any performance claim. Skepticism, too, increases with age. Remember Bernie Madoff, who promised a safe and sure 11% per year? Remember the dot.coms that were going ‘to the moon’ in 1999? If you didn’t believe it, you just ‘didn’t get it.’
And there is still the biggest claim of all — that the insiders, who know their stocks better than you, will sell them to you so you can make the profits. You’ll make money, even while you sleep.
Most stocks never pay off for investors. Very, very few pay off in a big way. Why should they? How many companies are lasting successes? How many pay consistent, substantial dividends? There were hundreds of auto companies in the early 20th century. By mid-century, there were only the Big Three left.
And of thousands of cryptocurrencies launched in the early 21st century, how many are still relevant? Today, most of the market cap is crowded into the ten top coins.
You never know what will happen. But the time to buy is when the sellers are discouraged by years of losses, not when they expect further gains.
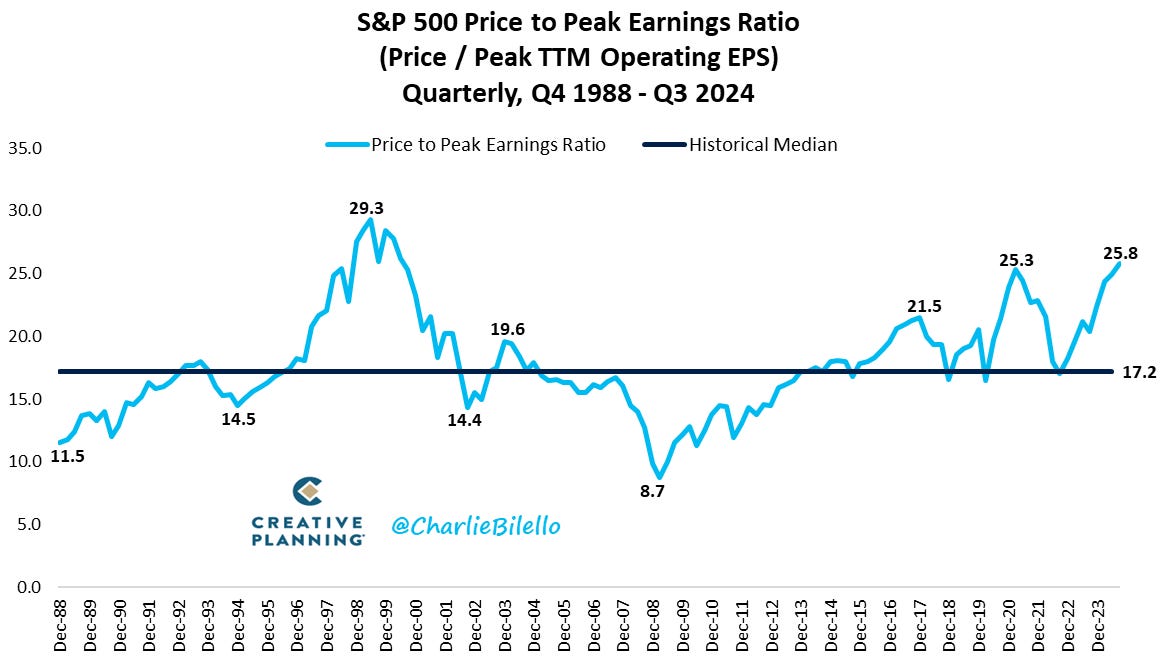
Today, stocks are expensive. They’re trading at 25 times S&P 500 earnings — about 50% above the historical mean. And high yield credit spreads haven’t been so low since 2007, indicating a fearlessness among investors that is almost always followed by under-performance in both stock and bond markets for years ahead.
Wall Street’s claims that you always make money in the stock market is an exaggeration. You make money sometimes, not all the time. Is one of those losing periods coming up soon?
We don’t know, but if you’re over 50, it’s too great a risk to ignore.
Regards,
Bill Bonner



